In this blog post, we will analyze the thermal performance of windows and provide you with a comprehensive understanding.
Picture this: it’s a cold winter night, and you’re snuggled up on the couch with a blanket and a hot cup of cocoa. As you look out your window, you notice that despite having the heat cranked up, your room still feels chilly.
You might be wondering what’s causing this discomfort – could it be your windows?
As someone who writes about house windows, I can tell you that thermal performance is one of the most critical factors to consider when choosing new windows for your home. The ability of a window to insulate against heat loss or gain can make all the difference in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures while also reducing energy bills.
In this blog post, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of thermal performance for windows. We’ll discuss how it works, what factors affect it, and why it matters so much for homeowners like yourself.
So sit back and grab another cup of cocoa – by the end of this post, you’ll be an expert on all things related to window insulation!
Heat Transfer Mechanisms

Now that we understand the importance of thermal performance for windows, let’s dive into how it works. To do this, we need to first understand the three mechanisms of heat transfer: conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction is when heat moves through a solid material like glass or wood. In terms of windows, this means that if your window frame is made from a poor insulating material such as aluminum or steel instead of vinyl or fiberglass frames with insulated cores then more heat will be lost through the frame.
Convection occurs when heated air rises and cooler air sinks creating currents in an enclosed space like your home. This can cause drafts around poorly sealed windows which allow cold outside air to enter while warm inside air escapes outwards.
Radiation refers to energy emitted by objects in all directions including towards other objects nearby (like walls). Windows can absorb radiant energy from sunlight during hot summer months causing indoor temperatures to rise significantly unless they are equipped with low-e coatings designed specifically for blocking solar gain.
Understanding these mechanisms helps us better appreciate why thermal performance matters so much for homeowners looking to keep their homes comfortable year-round without breaking the bank on heating and cooling bills!
Window Materials & Design
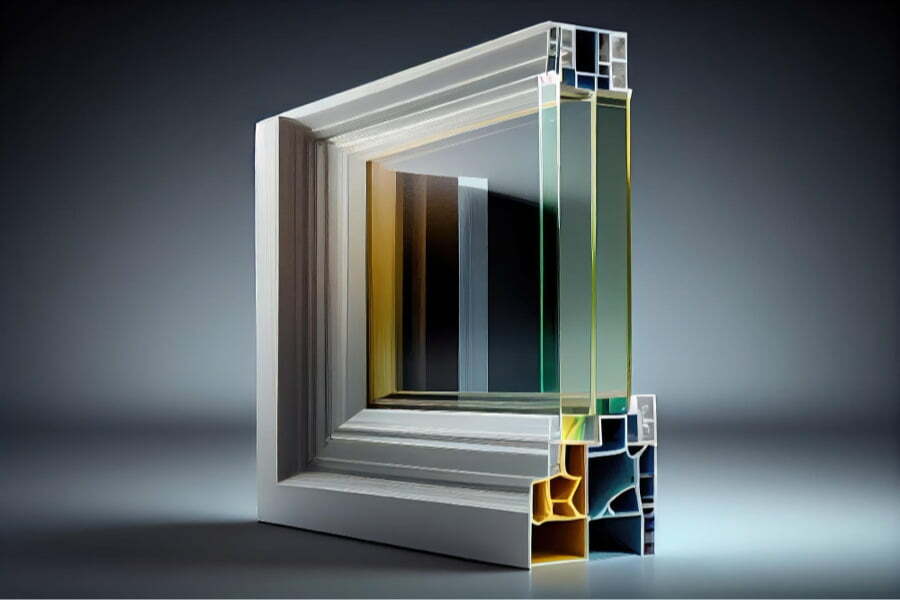

When it comes to thermal performance, the materials and design of a window play a crucial role. Different materials have varying levels of insulation properties, which can affect how well they keep heat inside or outside your home.
For example, vinyl windows are known for their excellent insulation capabilities due to their multi-chambered frames that trap air and prevent heat transfer. On the other hand, aluminum windows are not as effective at insulating because metal is an excellent conductor of heat.
However, advancements in technology have allowed manufacturers to create thermally broken aluminum frames that include a layer of non-conductive material between the interior and exterior parts of the frame. Window design also plays an important role in thermal performance.
Double-paned or triple-paned glass with low-emissivity coatings can significantly reduce energy loss by reflecting radiant heat back into your home while blocking UV rays from entering through your windows. By understanding these factors when choosing new windows for your home, you’ll be able to make informed decisions about which materials and designs will provide optimal thermal performance – keeping you cozy on those cold winter nights without breaking the bank on heating bills!
Glazing Technologies

When it comes to thermal performance, the type of glazing used in a window can have a significant impact. Glazing refers to the glass or plastic panes that make up the window, and there are several different technologies available on the market today.
One popular option is double-glazed windows, which consist of two panes of glass separated by an insulating layer. This design helps reduce heat transfer between indoors and outdoors while also providing some sound insulation benefits.
Another technology gaining popularity is low-emissivity (low-e) coatings. These coatings are applied directly to one or more surfaces of the glazing and help reflect infrared radiation back into your home while allowing visible light through.
Triple-glazed windows offer even greater insulation than double-glazed options by adding an additional pane of glass with another insulating layer in between them.
As you can see, there are many different types of glazing technologies available for homeowners looking to improve their home’s thermal performance. By understanding these options and working with a knowledgeable professional installer like myself as someone who writes about house windows – you’ll be able to choose new windows that will keep your home comfortable all year round without breaking your budget!
Insulation Techniques
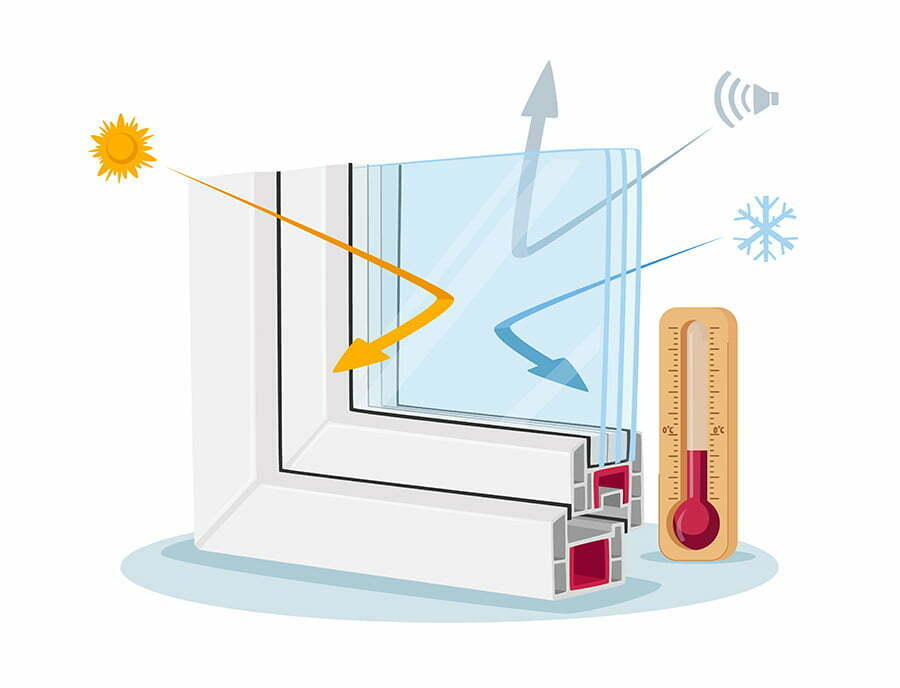
When it comes to thermal performance, the insulation technique used in a window plays a crucial role. There are several methods that manufacturers use to improve the insulating properties of windows, including double glazing and low-emissivity coatings.
Double glazing involves using two panes of glass with an air gap between them. This air gap acts as an insulator by reducing heat transfer through conduction and convection.
The wider the gap between the panes, the better its insulation properties.
Low-emissivity (low-e) coatings are another popular method for improving thermal performance in windows. These thin metallic layers reflect infrared radiation back into your home while allowing visible light to pass through – this means that they can help keep your home warm during winter months while also blocking out harmful UV rays during summer months.
By understanding these different techniques used for window insulation, you’ll be able to make informed decisions when choosing new windows for your home based on their energy efficiency ratings and overall cost-effectiveness. So if you’re looking forward to enjoying cozy winter nights without worrying about high energy bills or chilly drafts from poorly insulated windows – consider investing in double-glazed or low-e coated options!
Energy Efficiency Ratings
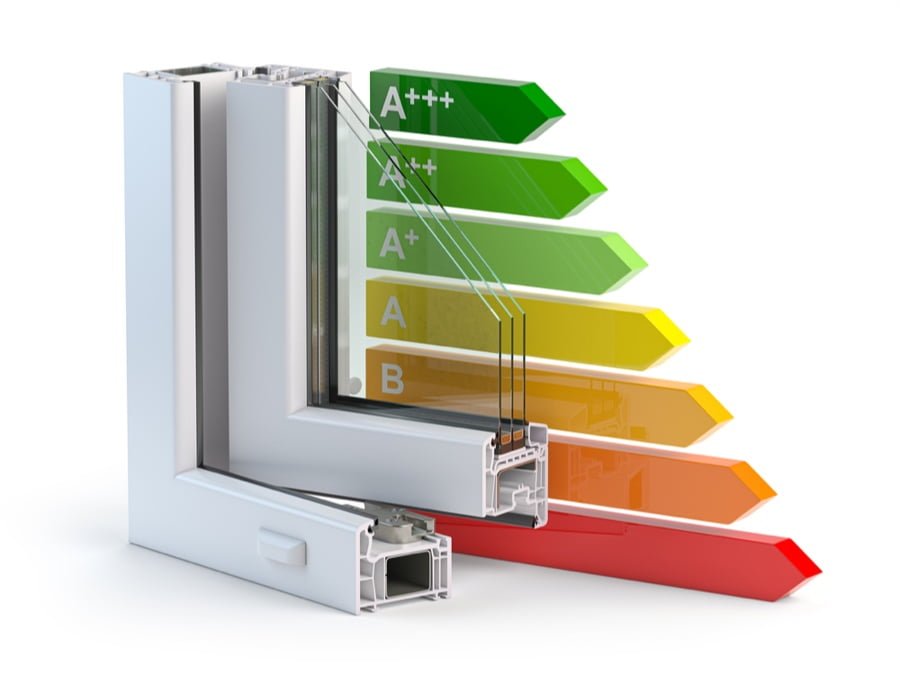

When it comes to choosing new windows for your home, one of the most important factors to consider is energy efficiency. This is where Energy Efficiency Ratings (EER) come into play.
EERs are a measure of how well a window can insulate against heat loss or gain and are determined by various factors such as the type of glass used, frame material, and overall design.
As I mentioned earlier in our story, you might have noticed that despite having your heating system on full blast during winter nights; you still feel chilly inside your room. The reason behind this could be due to poor thermal performance from your windows leading to heat loss through conduction or radiation.
By selecting high EER rated windows for their homes, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy bills while also maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year. Windows with higher ratings will typically feature double-paned glass with low-emissivity coatings that reflect radiant heat back into the room instead of allowing it to escape outside.
When shopping for new windows always look out for Energy Efficiency Ratings as they provide an accurate indication of how well a window will perform in terms of insulation and help save money on utility bills over time!
Thermal Bridging Analysis

Now that we understand the importance of thermal performance for windows, let’s dive deeper into one critical aspect: thermal bridging analysis. Thermal bridging occurs when a material with high conductivity (such as metal) connects the interior and exterior surfaces of a window frame, allowing heat to transfer through it more easily than other parts of the window.
This can lead to significant energy loss and discomfort in your home during extreme weather conditions. To avoid this issue, manufacturers use various techniques such as insulating materials or designing frames with lower conductivity materials like vinyl or fiberglass.
When choosing new windows for your home, it’s essential to consider their thermal bridging potential carefully. Look for products that have undergone rigorous testing and certification processes such as ENERGY STAR® ratings or NFRC labels indicating U-factor values – these will help you make an informed decision about which windows are best suited for your needs.
By understanding how different factors affect thermal performance in windows – including framing material choice and insulation methods – you’ll be able to choose products that provide optimal comfort while also saving on energy costs over time.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
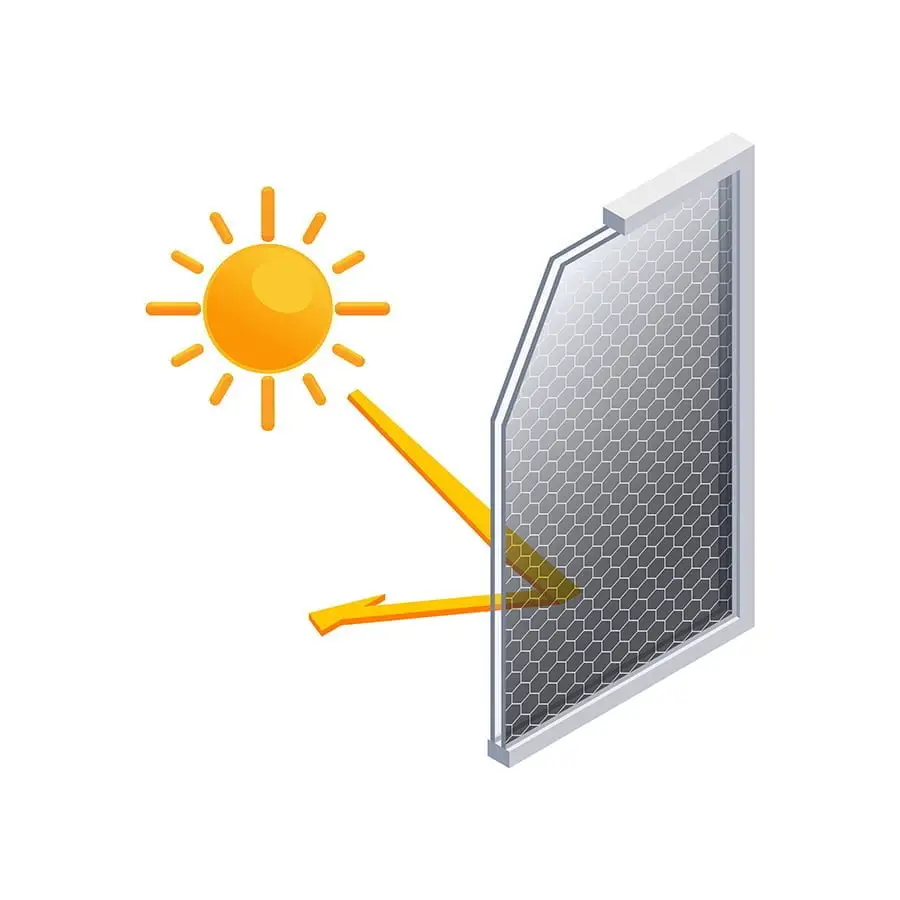

As we discussed in the introduction, thermal performance is a crucial factor to consider when choosing new windows for your home. One of the key metrics used to measure this performance is called Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC).
This metric measures how much solar radiation passes through a window and enters your home as heat. A high SHGC means that more solar radiation will enter your home, which can be beneficial during colder months but may lead to overheating during warmer months.
On the other hand, a low SHGC means less solar radiation will pass through and enter your home – ideal for hotter climates or south-facing windows that receive direct sunlight throughout most of the day. When selecting new windows for their homes, many homeowners focus solely on factors such as insulation or U-factor while overlooking important metrics like SHGC.
However, understanding how these different metrics work together can help you make an informed decision about which type of window best suits both your climate zone and personal preferences.
Don’t overlook Solar Heat Gain Coefficient when considering thermal performance! It’s just one piece of the puzzle but plays an essential role in keeping you comfortable year-round while also reducing energy bills.
Recap




